Link farming is an unethical link-building practice that website owners use to quickly acquire backlinks. It involves creating a network of low-quality websites that heavily link to one another to manipulate search engine rankings.
Google has spam policies to curb practices that negatively impact search engine rankings. One of them is expired domain abuse, which involves repurposing an expired domain with a high DA to build links to a new website to improve rankings.
Some of the link farm websites may be using this tactic, which means Google is likely to devalue the ranking power of each link you get from them.
In any case, link farming is a risky practice that will ultimately hurt your SEO and credibility. Read on to identify the dangers of link farming and learn what you should do instead for your long-term success.
What Is A Link Farm
Link farms are a network of interlinked websites created solely to acquire backlinks and manipulate search engine rankings.
Here are the domain, backlink profile, and other SEO metrics of a link farm website. While the site has a high domain rating (DR) and over 25K backlinks, it has suspiciously low organic traffic (as you can see in the report below).
Most search engines’ webmaster guidelines may penalize link farms and their linked domains. So, you mustn’t try to deceive search engines by building inbound links from any link farms.
People often confuse link farms with web directories and private blog networks (PBNs). So, here is a glance at how they differ:
How To Identify Or Spot A Link Farm
Identifying link farms correctly is important so that you don’t indulge in reciprocal linking or building inbound links from those websites. Here are some techniques to help you identify a link farm website and avoid acquiring backlinks from it:
Evaluate the overall content quality of the website
Link farms are websites with low-quality content or unrelated content from multiple niches.
Analyze the website from which you want to build links pointing to your website for quality issues. Websites with poorly written, thin, duplicate, or AI-generated content that offers little value to users are likely to be link farms. They are created solely for keyword-rich link exchanges.
Similarly, if a website has content that seems irrelevant and covers random topics, that’s also a sign of it being part of a link farm. Scroll through the blog section of your target website to identify this.
Here’s a screenshot from a website that publishes poor-quality content on unrelated niches like medical science, digital marketing, and travel recommendations:
Verify the author’s information on the website
Link farm websites often feature anonymous authors or display fake author profiles accompanied by generic stock photography. So, if a website doesn’t disclose author information clearly, that’s a red flag.
Genuine websites display author bios and showcase links to the author’s personal blog and social media profiles for authenticity. Many of them have comprehensive author pages like the example below.
Check the number of linked websites
While linking to a relevant and authoritative site is good SEO practice, a red flag is when a website links out to a large number of unrelated websites, especially those with low domain authority (DA).
Does the website feature numerous suspicious, low-quality outbound links to unrelated websites? Then, it is likely a link-farming website. Some of these websites have entire pages that consist solely of lists of outgoing links without context.
Conduct a backlink audit of the website
Analyze the website’s backlink profile using SEO tools like Semrush or Ahrefs. It will help you check the number and quality of backlinks, anchor texts, referring domains, and other relevant metrics.
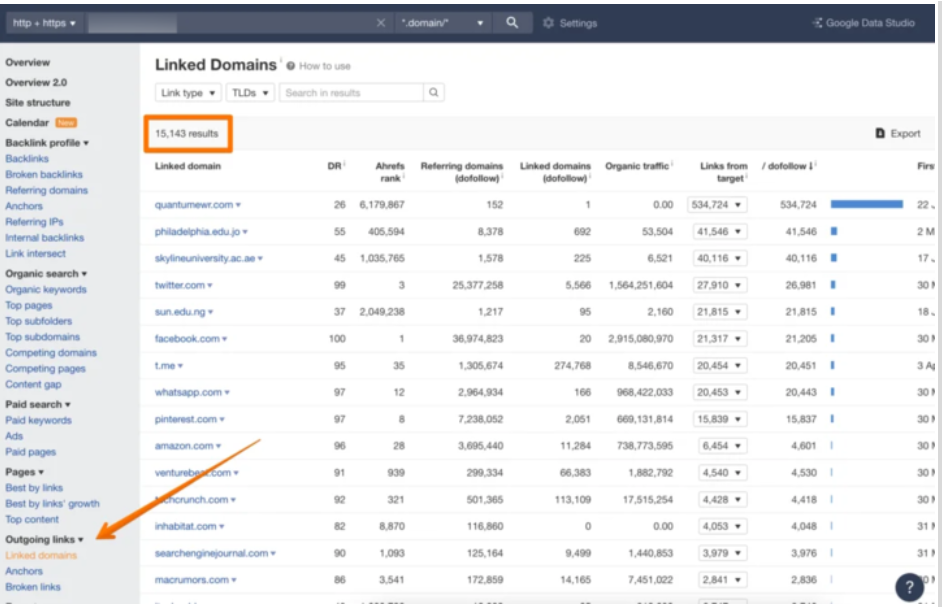
For example, see the Ahrefs backlink report, which showcases backlinks from pages in different languages and on various topics, all using the exact anchor text. This appears suspicious and suggests link farming.
Flag sudden increases in the number of backlinks
A sudden increase in the number of backlinks to a website indicates the use of unethical link-building practices like link farming. You should also check for a boost in incoming and outgoing links from other websites that could be part of private blog networks.
You can use an SEO tool like Ahrefs to check for a sudden spike in the number of backlinks or referring domains.
Look for backlinks from suspicious websites
If a website has links from suspicious websites or websites from completely unrelated niches, then it likely is a link farm.
There are too many do-follow links from one website, which looks suspicious as well.
Analyze the anchor texts for outbound links on the website
Link farms don’t often bother with using relevant anchor texts or even relevant links. So, if you spot a website with too many links on generic anchor texts, such as “click here” or “learn more,” then that’s a bad sign.
Also, if a website has too many links on just a few keyword-specific anchor texts, then it’s most likely a link farm. You can also detect link farms by empty anchor texts.
Flag rapid fluctuations in the website’s search rankings and organic traffic
If you suspect a website to be a link farm, check the site’s rankings in search results over time. Any sudden increase or regular fluctuations in its rankings on search engine results pages indicate the use of link farms and other black hat SEO techniques.
Assess the look and feel of the website
Manually visit the website and check out its layout and design. Websites that are a part of link farms often use templates with little or no customization and look messy. So, they are easier to spot.
- Look for networks of interlinking websites with little original content
In link farms, the websites frequently add links to each other, building a network of interconnected links and pages. Look for websites with low-quality content that heavily link to a specific set of websites to identify a link farm.
Identify paid link offers and schemes
If you spot websites that claim to build you high-quality backlinks at low cost, stay away from those. Often, these are part of paid link schemes, and associating with them is not good for your website’s SEO.
So, don’t fall for link schemes like this:
5 Reasons To Avoid Link Farms (How It Can Hurt Your Website’s SEO)
Let’s take a look at some dangers of link farming and why you should avoid link farms for your link building campaigns from the start. We’ll explore how dangerous these links could be for a site’s backlink profile and domain authority.
Your website can incur penalties from search engines
Google and other search engines are against link farms and recognize it as a spammy link building technique. After the Google Penguin update, Google’s algorithms have become more adept at identifying such practices.
If caught using link farming, your website could receive a penalty or lose your rankings in search results.
Even if the search engine algorithms fail to identify link farms, human reviewers may detect it and impose a manual action on your website. Once penalized, your website will take a long time to recover from it and build authority again.
It can lead to de-indexing of your website
Well know that a search engine indexes your new content and pages and then ranks them on its results pages for related queries. However, the same search engine can also de-index your website and remove your site from appearing in the search results pages all together if your site is caught acquiring links from link farms.
This means that getting your site penalized and losing your current rankings aren’t the worst consequences of building link farms links. De-indexation is a situation that could be extremely difficult to recover from. It makes link farming a risky practice.
It can hurt your search engine rankings
There are several ways in which using link farms can hurt your visibility on the search engines. Here are a few of them:
You build low-quality links using a link farm and Google lowers your search rankings rankings.
You get caught and Google imposes penalties, which hurt your website’s authority and rankings in search results, or you get completely removed from its index.
You get penalized and recover from the penalty, but it takes a hit on your reputation and your website gets devalued by Google.
It can cause long-term damage to your website’s credibility and reputation
If your website is caught using link farms and receives a penalty, it can severely damage your website’s authority and reputation. In some cases, Google can flag your website as spam for not following its search engine guidelines, hurting your website’s credibility.
It also causes your website’s users to think of your site as non-trustworthy. This can significantly affect traffic and rankings.
You’ll end up wasting time and resources
The links built using link farms are typically low-quality backlinks that don’t serve much purpose in the long run. While this may boost the number of backlinks, it will weaken your link profile.
So, you spend time and money and still don’t see long-term positive results. It’s more effective to spend that time and money on ethical SEO practices that drive sustainable results over time.
What Should You Do Instead? Link Building Best Practices
Follow these best practices to build high-quality links without falling prey to link farms:
- Don’t try to acquire links in bulk. Focus on quality.
- Create high-quality content to acquire high-quality backlinks that adhere to the search engine guidelines.
- Use ethical link building practices, such as publishing relevant guest posts, participating in expert roundups, and reclaiming broken links or unlinked mentions.
- Reach out to reputable websites within your niche and collaborate with them to build backlinks to relevant content using appropriate anchor texts.
- Work with influencers or affiliates to gain brand mentions and high-quality links from product reviews and other useful content.
- Regularly conduct backlink audits to find and disavow toxic backlinks to improve your link profile. Ensure your site only has links from legitimate websites.
- Follow Google’s webmaster guidelines and refrain from using practices that go against it.
Ready To Protect Your Website From Link Farms?
Link farming is a risky, black-hat SEO technique that may deliver quick results but is extremely harmful in the long run. If caught using link farming, your website may get penalized, devalued, or deindexed.
What should you do instead? Use our contextual link building and SEO services to build backlinks ethically from high-quality content on relevant websites. We’ll help ensure the good health of your link profiles by earning links that matter to your business.




